Did you know that over 90% of modern computer screens use either LED or LCD technology? While they may appear similar, LED and LCD monitors differ significantly in picture quality, energy efficiency, design, and price. Understanding these differences can help you pick the perfect monitor for your needs—whether for work, gaming, or entertainment. In this guide, we break down everything you need to know in a simple and clear way.
Read More: https://newsokay.com/unlocking-the-power-of-authentication/
Table of Contents
- LED vs LCD Monitors: Key Differences
- Full Forms and What They Mean
- Backlight Technology
- Picture Quality
- Power Consumption
- Design and Thickness
- Color Display
- Viewing Angles
- Lifespan
- Price Comparison
- Best Use Cases
- FAQs About LED vs LCD Monitors
LED vs LCD Monitors: Key Differences
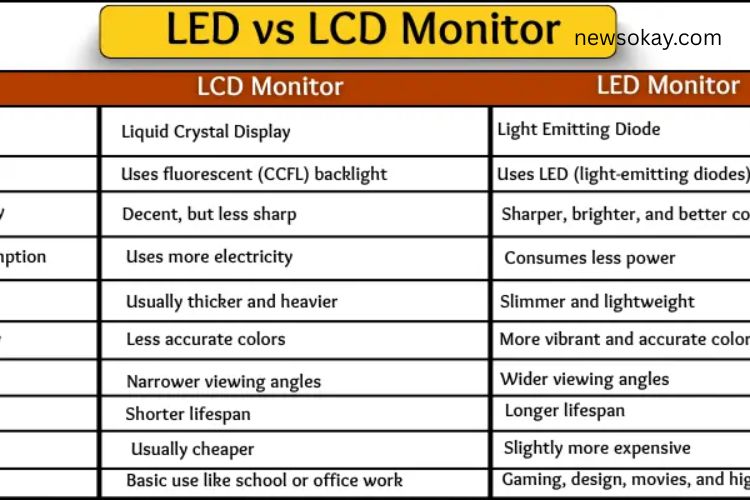
Many people confuse LED and LCD monitors, assuming they are the same. While both are popular, their technology is quite different. LED monitors use light-emitting diodes, whereas LCD monitors rely on liquid crystal displays combined with fluorescent backlights. These differences impact everything from screen clarity to energy consumption and price.
Full Forms and What They Mean
Understanding the full forms helps clarify their function:
LED Monitor:
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. These tiny lights illuminate the screen, providing bright, sharp images while consuming less energy. LED monitors deliver superior visual performance and are commonly used in modern displays.
LCD Monitor:
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display. This technology uses a special liquid to display images. LCD screens require a fluorescent backlight to work, which uses more energy and produces slightly less vivid colors. They are still widely used for basic tasks.
Backlight Technology
The backlight is where LED and LCD monitors differ the most:
LED Monitors:
LEDs are small, bright lights that sit behind or around the screen. They turn on instantly and consume minimal power, enhancing contrast and sharpness.
LCD Monitors:
LCD screens use fluorescent tubes as backlights. These tubes take more space, consume more electricity, and produce less brightness compared to LEDs. As a result, LCD monitors often appear thicker and less vivid.
Picture Quality
Picture quality determines how clear and vibrant a monitor appears:
LED Monitors:
LED screens deliver brighter, sharper images with better contrast. Dark areas look deeper, and bright areas pop, making movies, games, and graphics more enjoyable.
LCD Monitors:
LCD monitors produce adequate images but with lower contrast and slightly muted colors. They are fine for general tasks but fall short for gaming or graphic-intensive work.
Power Consumption
Energy efficiency is crucial, especially if you use your monitor for hours daily:
LED Monitors:
LEDs consume less power due to their efficient design, saving money on electricity bills and contributing to eco-friendly usage.
LCD Monitors:
LCDs require more power to operate fluorescent backlights, making them less energy-efficient compared to LEDs.
Design and Thickness
Monitor design is influenced by backlighting:
LED Monitors:
LEDs are compact, allowing the monitors to be slim, lightweight, and modern-looking. Their sleek design makes them ideal for stylish home and office setups.
LCD Monitors:
Fluorescent tubes in LCDs require extra space, making these monitors thicker and heavier. While functional, they lack the slim, contemporary design of LED monitors.
Color Display
Color accuracy and vibrancy are vital for enjoyable viewing:
LED Monitors:
LEDs provide vivid, realistic colors. Images appear sharp and lively, which is perfect for watching movies, editing photos, or gaming.
LCD Monitors:
Colors on LCD screens are softer and slightly muted. They still work for basic browsing, typing, or document work but don’t deliver the same punch as LEDs.
Viewing Angles
A monitor’s viewing angle affects how well images are seen from the side:
LED Monitors:
LEDs maintain clear and consistent colors even when viewed from an angle. Multiple people can comfortably watch the screen without distortion.
LCD Monitors:
LCDs perform best when viewed directly. From the side, the screen may look darker or faded, limiting its suitability for group viewing.
Lifespan
Monitor longevity depends on the type of backlight used:
LED Monitors:
LEDs generate less heat, resulting in longer lifespan and reliable performance over several years. They are less prone to damage from prolonged use.
LCD Monitors:
Fluorescent backlights in LCDs produce more heat, which can shorten lifespan. LCD monitors may require replacement sooner than LEDs.
Price Comparison
Price is often a deciding factor:
LED Monitors:
LED monitors are more expensive due to advanced technology, superior brightness, and better design. Many professionals and gamers find the investment worthwhile.
LCD Monitors:
LCDs are cheaper and widely used in schools, offices, and home setups. If your budget is limited, LCD monitors provide basic functionality at an affordable cost.
Best Use Cases
Different monitors suit different needs:
LED Monitors:
- Ideal for gaming and movie watching
- Preferred by graphic designers and video editors
- Perfect for modern home or office setups
LCD Monitors:
- Suitable for basic tasks like typing, browsing, and schoolwork
- Cost-effective choice for offices or budget-conscious users
- Adequate for general home use
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the main difference between LED and LCD monitors?
LED monitors use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, offering brighter colors, better contrast, and energy efficiency, while LCD monitors use fluorescent lights, which are thicker, less vivid, and consume more power.
Which monitor is better for gaming?
LED monitors are ideal for gaming because they provide faster response times, sharper images, and vibrant colors that enhance the gaming experience.
Are LED monitors more expensive than LCD?
Yes, LED monitors typically cost more due to advanced technology, better picture quality, and slimmer, modern designs.
Can LCD monitors be used for office or home work?
Absolutely. LCD monitors are budget-friendly and sufficient for tasks like typing, browsing, and watching videos.
Which monitor lasts longer?
LED monitors usually have a longer lifespan because LEDs generate less heat and are more durable than traditional fluorescent backlights used in LCD monitors.
Do LED monitors save electricity?
Yes, LED monitors are more energy-efficient, helping reduce electricity costs compared to LCD monitors.
Which monitor offers better color accuracy?
LED monitors deliver more vivid, sharp, and realistic colors, making them perfect for movies, graphic design, and video editing.
Conclusion
Choosing between an LED and LCD monitor depends on your priorities, budget, and intended use. LED monitors excel in brightness, color accuracy, energy efficiency, and sleek design, making them perfect for gaming, movies, and professional work. LCD monitors, on the other hand, are cost-effective and reliable for basic office tasks, browsing, and home use. By understanding their differences, you can select the monitor that delivers the best viewing experience for your needs, whether at home, in the office, or for gaming.