- What Makes Up a Computer Network?
- Hub
- Switch
- Router
- Modem
- Access Point (AP)
- Cables (Ethernet)
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Server
- Client (Workstation or PC)
- How These Components Work Together
- Frequently Asked Questions:
- What are the main components of a computer network?
- What is the difference between a hub and a switch?
- How does a router differ from a modem?
- Why is a firewall important in a network?
- What role does an access point (AP) play in networking?
- What is a Network Interface Card (NIC)?
- What is the function of a server in a network?
- Conclusion
A computer network is more than just connecting devices—it is a complex ecosystem where hardware and software work together to transmit data, share resources, and enable communication. Every network, whether for home, school, or office, relies on essential components to function efficiently. Understanding these components helps businesses, IT professionals, and tech enthusiasts design, manage, and optimize networks effectively.
Read More: https://newsokay.com/revolutionize-your-printing-experience-today/
What Makes Up a Computer Network?
A computer network consists of interconnected devices and infrastructure that allow data to flow seamlessly between computers, servers, and other hardware. Without these components, devices cannot communicate, share files, or access the internet. Each element has a unique role, ensuring smooth operation, faster data transfer, and security.
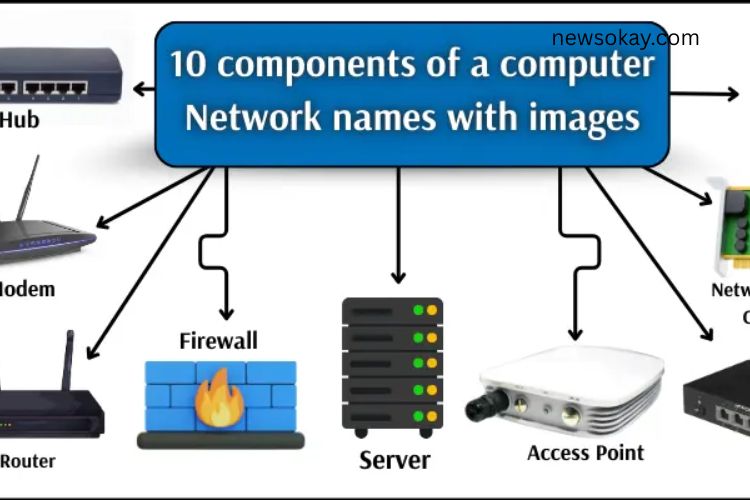
Here are the 10 key components of a computer network that form the backbone of connectivity:
Hub
A hub is a basic network device that connects multiple computers in a network. When one computer sends data, the hub broadcasts it to all connected devices. While simple, hubs are ideal for small networks or learning environments.
Advantages:
- Connects multiple computers quickly
- Easy to install and use
- Affordable for small networks
- Helps beginners understand networking basics
Example: A small office with 5 computers can use a hub to share files simultaneously across all devices.
Switch
A switch is smarter than a hub. It connects multiple devices but only sends data to the intended recipient, reducing network congestion and collisions. Switches are essential for medium to large networks where efficient communication is critical.
Advantages:
- Directs data only to the correct device
- Improves network speed and efficiency
- Reduces data collisions
- Easy to install and manage
Example: An office with 20 computers can use a switch to ensure each file is delivered to the right device without slowing down the network.
Router
A router connects different networks and directs data between them. It enables multiple devices to share a single internet connection and selects the fastest path for data transfer. Routers also provide basic security and improve overall network performance.
Advantages:
- Connects multiple networks efficiently
- Directs data along the fastest route
- Supports multiple devices simultaneously
- Offers basic security features
Example: At home, a router allows laptops, smartphones, and smart TVs to connect to the internet together.
Modem
A modem links a network to the internet. It converts digital data from a computer into signals that travel over phone lines or cable systems, then translates incoming signals back into digital form.
Advantages:
- Provides internet connectivity
- Converts data for communication over cables or phone lines
- Easy for beginners to set up
- Ensures reliable internet access
Example: A cable modem allows laptops and smartphones at home to access the internet simultaneously.
Access Point (AP)
An access point enables wireless devices to join a network. It bridges wireless devices like laptops, tablets, and smartphones with the main wired network, expanding coverage and improving mobility.
Advantages:
- Connects wireless devices to the network
- Extends network coverage
- Easy to install and manage
- Enhances flexibility and mobility
Example: In schools, access points allow students to connect tablets to the school network and access online resources seamlessly.
Firewall
A firewall is a security component that monitors incoming and outgoing data, blocking threats such as malware, viruses, or unauthorized access. Firewalls protect networks in homes and offices, ensuring safe data transfer.
Advantages:
- Protects networks from hackers and malware
- Controls which data can enter or leave the network
- Maintains sensitive data security
- Enhances overall network performance
Example: An office firewall prevents employees from accessing harmful websites and protects company data.
Cables (Ethernet)
Ethernet cables and other wired connections transmit data between devices. They provide a reliable, high-speed connection essential for many business and home networks.
Advantages:
- Fast and stable data transfer
- Minimal interference compared to wireless connections
- Easy to install in offices or homes
- Supports large volumes of data
Example: Computers in an office can connect to a switch via Ethernet cables for efficient file sharing.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware component that enables a device to connect to a network, either wired or wireless. NICs are vital for network participation and communication.
Advantages:
- Connects computers to networks effortlessly
- Compatible with wired and wireless networks
- Essential for building any network
Example: A laptop with a NIC can connect to Wi-Fi or Ethernet to access the internet and share files.
Server
A server is a specialized computer that stores data, manages applications, and provides resources to other computers in the network. Servers centralize resources, making networks more organized and efficient.
Advantages:
- Central storage and management of data
- Runs applications for multiple devices
- Streamlines resource sharing
- Improves network reliability and performance
Example: A company server stores employee files, allowing everyone to access the information from their devices.
Client (Workstation or PC)
A client is any computer or device that accesses data and services provided by a server. Clients send requests to servers and receive responses, making network collaboration possible.
Advantages:
- Accesses data and applications from the network
- Enables smooth communication with servers
- Supports productivity and collaboration
- Works in small and large networks
Example: An employee’s desktop computer accesses files stored on the office server, enabling efficient workflow.
How These Components Work Together
A computer network operates efficiently when all components function cohesively. Hubs and switches manage data flow, routers and modems handle external communication, and servers store and distribute information. Clients and access points allow users to interact with the network, while NICs and cables provide physical connectivity. Firewalls secure the network, ensuring data moves safely and reliably.
Together, these components create a network that is:
- Fast and reliable
- Secure against threats
- Scalable to accommodate growth
- Flexible for wired and wireless connections
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the main components of a computer network?
The main components include hubs, switches, routers, modems, access points, firewalls, cables, network interface cards (NICs), servers, and client devices. Each plays a critical role in enabling communication and data sharing.
What is the difference between a hub and a switch?
A hub sends data to all connected devices, while a switch directs data only to the intended recipient, reducing network congestion and improving speed.
How does a router differ from a modem?
A modem connects your network to the internet by converting digital signals, while a router directs data between devices and networks, allowing multiple devices to share the same connection.
Why is a firewall important in a network?
Firewalls protect networks from unauthorized access, malware, and cyberattacks. They monitor incoming and outgoing traffic to maintain security and data integrity.
What role does an access point (AP) play in networking?
Access points allow wireless devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets to connect to a wired network, extending coverage and improving mobility for users.
What is a Network Interface Card (NIC)?
A NIC is a hardware component that allows a computer or device to connect to a network, supporting both wired and wireless connections.
What is the function of a server in a network?
Servers store data, manage applications, and provide resources to client devices, ensuring smooth operation and centralized data management.
Conclusion
Understanding the essential components of a computer network is crucial for building efficient, secure, and reliable connectivity. From hubs and switches to routers, modems, and firewalls, each element plays a vital role in ensuring smooth communication, fast data transfer, and network protection. Whether for home, office, or enterprise environments, leveraging these components effectively allows users to maximize productivity, enhance collaboration, and maintain robust network performance. By mastering how these components work together, you can design networks that are scalable, flexible, and prepared for the demands of today’s digital world.