- What Are Storage Devices?
- A Brief History of Storage Devices
- How Storage Devices Work
- Importance of Storage Devices
- Types of Storage Devices
- Uses of Storage Devices
- Key Features of Storage Devices
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Storage Devices
- Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is a computer storage device?
- Why are storage devices important for computers?
- How does an HDD differ from an SSD?
- What is cloud storage, and how does it work?
- Can storage devices fail, and how can I prevent data loss?
- Which storage device is best for gaming?
- What is the difference between primary and secondary storage?
- Conclusion
Computer storage devices are essential tools that allow users to save, access, and manage data efficiently. From photos and videos to software and important documents, storage devices ensure that all digital information remains secure and readily available. Without these devices, computers would be unable to retain any data, making modern computing impossible. Understanding storage devices, their history, types, and functions is crucial for anyone looking to maximize their computer’s performance and manage data effectively.
Read More: https://newsokay.com/led-vs-lcd-monitors-discover-the-ultimate/
What Are Storage Devices?
Storage devices are components that save digital information in a computer or other electronic device. They allow users to store data permanently or temporarily, ensuring it can be retrieved whenever needed. These devices come in various forms, from traditional hard drives to cutting-edge solid-state drives and cloud storage solutions.
Storage devices serve multiple purposes:
- Safe Data Storage: Keep files secure for long-term use.
- Quick Access: Open and use data efficiently.
- Data Backup: Prevent data loss by creating copies.
- File Transfer: Move data between devices with ease.
- Large Capacity: Store vast amounts of data.
- Data Sharing: Easily share files via USB or cloud services.
A Brief History of Storage Devices
Computer storage has evolved significantly over the past several decades. Early storage devices were limited in capacity and speed, but advancements in technology have made modern storage faster, larger, and more reliable.
1950s: Magnetic Tapes
Magnetic tape was one of the earliest storage methods, capable of storing large volumes of data on reels. Despite its size, tape storage was slow and cumbersome.
1960s: Punch Cards
Punch cards stored data by encoding information into patterns of holes on cards. They were used primarily in large mainframe computers.
1970s: Floppy Disks
Floppy disks made data storage portable and convenient. Available in sizes like 5.25 inches and 3.5 inches, they allowed users to save and transport files easily.
1980s: Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
Hard disk drives became widely used, offering faster storage and retrieval than floppy disks. They could store significantly more data and became the standard for desktop computers.
1990s: CD and DVD Storage
Compact Discs (CDs) and Digital Versatile Discs (DVDs) introduced optical storage for music, movies, and large data files. They were more durable and could store more data than earlier storage media.
2000s: USB Flash Drives and External HDDs
USB flash drives and external hard drives revolutionized portable storage. USB drives were small and convenient, while external HDDs allowed users to store massive amounts of data outside their computers.
2010s: Solid-State Drives (SSD) and Cloud Storage
Solid-state drives replaced HDDs in many computers due to their speed and reliability. Meanwhile, cloud storage emerged, enabling users to store data online and access it from anywhere, marking a significant shift in storage technology.
How Storage Devices Work
Storage devices operate by saving data in various formats and using different technologies to store and retrieve it. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Saving Data: Files, images, and videos are saved in a specific format.
- Storage Method: Devices store data using magnetic (HDD), electronic (SSD, USB), or optical (CD/DVD) methods.
- Data Retrieval: Devices locate and access the stored information. HDDs use a read/write head, while SSDs retrieve data instantly from memory chips.
- Data Access: Users can open, edit, or share their data whenever needed.
Importance of Storage Devices
Storage devices are vital for every computer user. They not only save data but also enhance performance and improve workflow. The key reasons storage devices matter include:
- Data Preservation: Protect files from accidental loss.
- Efficient Workflow: Quickly access and run software.
- Data Backup: Secure copies of important information.
- File Portability: Transfer data across devices easily.
- Ample Storage Space: Accommodate large files, apps, and media.
- Enhanced Sharing: Share information effortlessly via USB or cloud.
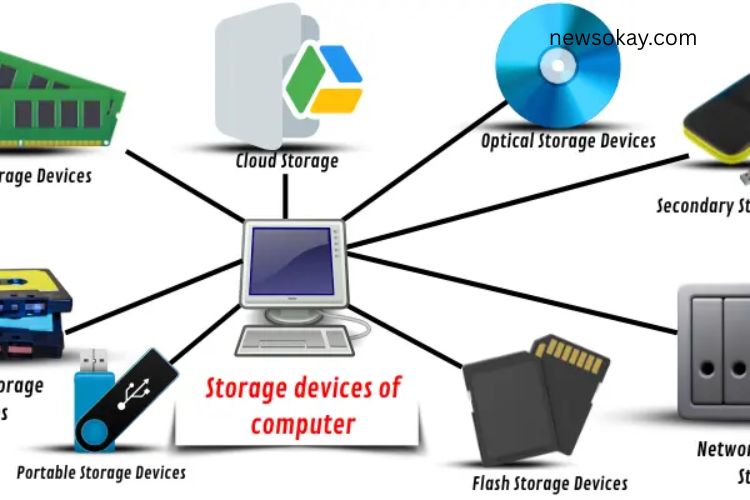
Types of Storage Devices
Computer storage devices vary in function, performance, and use case. They are categorized into several types:
Primary Storage Devices
These include RAM (Random Access Memory) and cache, which temporarily store data for immediate use.
Secondary Storage Devices
Devices like HDDs, SSDs, and USB drives store data permanently.
Tertiary Storage Devices
Used mainly in enterprise environments, these include tape drives and large optical storage systems for backup and archiving.
Optical Storage Devices
CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs use laser technology to store data.
Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
NAS systems allow multiple users to access shared data over a network, ideal for businesses.
Portable Storage Devices
USB drives, memory cards, and external SSDs provide on-the-go data access.
Cloud Storage
Stores data online, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Flash Storage Devices
SSD and USB drives use flash memory, providing fast, durable, and energy-efficient storage.
Uses of Storage Devices
Storage devices play a crucial role in various everyday activities:
- Saving Documents: Store work, school, and personal files.
- Backing Up Data: Prevent loss by saving multiple copies.
- Running Software: Install and run applications efficiently.
- Storing Photos and Videos: Keep memories safe and accessible.
- Gaming: Store games and related data for faster performance.
- Data Transfer: Move files between devices seamlessly.
- Entertainment: Store movies, music, and podcasts for offline use.
- Boosting Performance: SSDs improve computer speed significantly.
Key Features of Storage Devices
Storage devices come with features that enhance their functionality:
- Capacity: Ability to hold large amounts of data.
- Speed: Quick data access and retrieval.
- Portability: Easy to carry and use on multiple devices.
- Security: Protects against data loss and unauthorized access.
- Compatibility: Works across different devices and operating systems.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces for all skill levels.
- Cost-Effective: Offers a balance between price and performance.
- Reliability: Minimizes errors and ensures data safety.
- Efficiency: Fast and smooth operation for daily tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Storage Devices
While storage devices are indispensable, they come with both benefits and limitations.
Advantages
- Easy to use and manage data.
- Portable and convenient.
- High storage capacity.
- Fast data access and transfer.
- Protect data from loss or corruption.
- Compatible with multiple devices.
- Support data backups and archiving.
- Durable and long-lasting.
- Help organize digital files efficiently.
Disadvantages
- Susceptible to physical damage.
- Some devices have limited storage capacity.
- Data loss risk if not backed up.
- Certain devices can be expensive.
- Some require external power sources.
- Vulnerable to theft or hacking without proper security.
- Can become outdated quickly.
- Affected by malware or viruses.
- May require regular maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a computer storage device?
A storage device is hardware that saves digital data, allowing users to store files, software, and media for later access. Examples include hard drives, SSDs, USB drives, and cloud storage.
Why are storage devices important for computers?
They secure your data, allow fast access, help run software, enable file sharing, and provide backup solutions, making them essential for efficient computing.
How does an HDD differ from an SSD?
HDDs use spinning magnetic disks to store data, which is slower but cost-effective for large storage. SSDs use flash memory, providing faster data access, durability, and energy efficiency.
What is cloud storage, and how does it work?
Cloud storage saves data on remote servers accessible via the internet. It allows users to access, share, and back up data from any device anywhere.
Can storage devices fail, and how can I prevent data loss?
Yes, devices can fail due to physical damage, malware, or age. Prevent data loss by regularly backing up data to another device or cloud storage.
Which storage device is best for gaming?
SSDs are preferred for gaming due to faster load times, quick data access, and improved overall system performance compared to HDDs.
What is the difference between primary and secondary storage?
Primary storage (like RAM) is temporary and fast, used while the computer is running. Secondary storage (like HDDs or SSDs) is permanent and holds data even when the computer is off.
Conclusion
Computer storage devices are the foundation of modern computing, enabling users to save, access, and manage data efficiently. From early magnetic tapes to today’s lightning-fast SSDs and versatile cloud storage, these devices have evolved to offer speed, reliability, and convenience. Understanding the different types, features, and uses of storage devices empowers users to choose the right solution for their needs—whether it’s for gaming, work, media storage, or data backup. By leveraging the right storage technology, you can enhance your computer’s performance, safeguard important files, and enjoy seamless digital experiences. Investing in quality storage devices is not just about saving data—it’s about unlocking the full potential of your computer.